Why Do My Gums Bleed When Brushing? Causes & Solutions
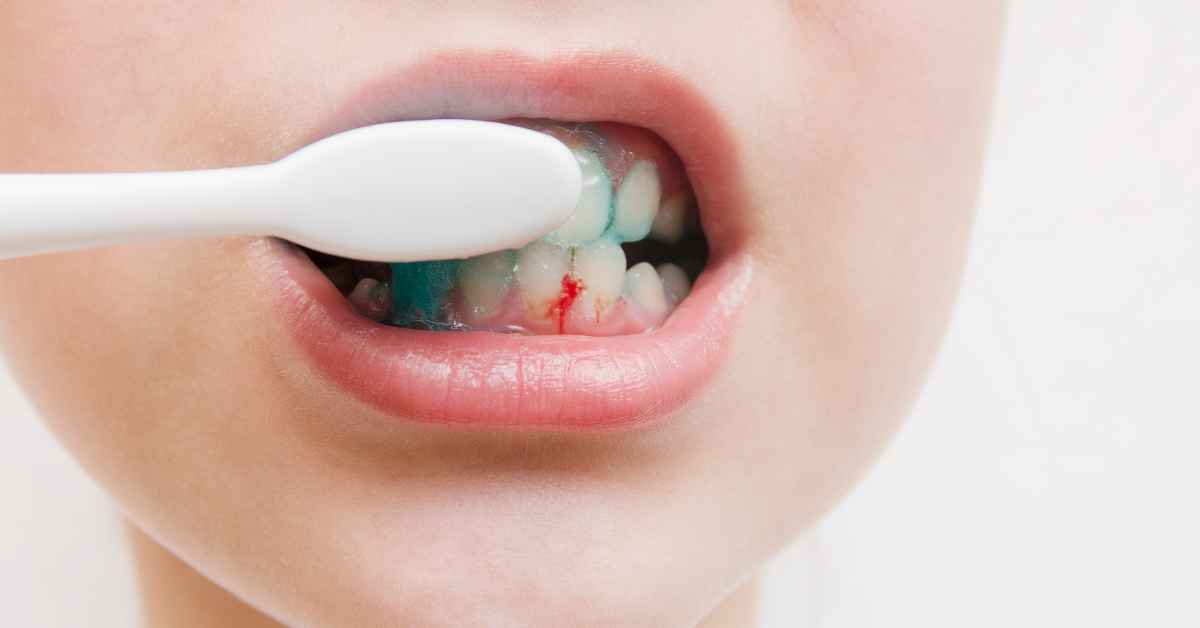
Noticing blood when you brush or floss your teeth can be worrying. Many people assume it’s normal or think they’re brushing too hard, but bleeding gums are often a sign that something isn’t quite right with your oral health. While occasional bleeding may not be serious, ongoing gum bleeding should never be ignored.
Understanding why your gums bleed and what you can do about it can help protect your teeth, gums, and overall health.
Is It Normal for Gums to Bleed When Brushing?
Healthy gums generally do not bleed. If your gums bleed regularly during brushing or flossing, it’s usually a sign of inflammation, irritation, or infection. In most cases, bleeding gums are an early warning sign of gum disease, but there are also other possible causes.
The good news is that bleeding gums are often reversible when addressed early with the right care and professional guidance.
Common Causes of Bleeding Gums
Gum Disease (Gingivitis and Periodontitis)
The most common cause of bleeding gums is gum disease.
- Gingivitis is the early stage and occurs when plaque builds up along the gumline, causing redness, swelling, and bleeding.
- Periodontitis is a more advanced form of gum disease that can lead to gum recession, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss if left untreated.
Bleeding during brushing is often one of the first signs that gum disease is developing.
Plaque and Tartar Build-Up
When plaque isn’t removed properly through brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar. Tartar irritates the gums and makes it harder to clean effectively at home, increasing inflammation and bleeding.
Brushing Too Hard or Using the Wrong Toothbrush
Aggressive brushing or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can damage delicate gum tissue. This can cause bleeding, soreness, and even gum recession over time.
Infrequent or Incorrect Flossing
If you don’t floss regularly, your gums may bleed when you start. This happens because plaque and bacteria have built up between the teeth. With consistent, gentle flossing, bleeding usually improves within a week or two.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, puberty, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding, even with good oral hygiene.
Certain Medical Conditions and Medications
Conditions such as diabetes, vitamin deficiencies (especially vitamin C), and blood disorders can contribute to bleeding gums. Some medications, including blood thinners, may also increase bleeding.
Why You Shouldn’t Ignore Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums aren’t just a dental issue they can affect your overall health. Research has shown a link between gum disease and conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. Inflammation in the gums allows bacteria to enter the bloodstream, potentially impacting other parts of the body.
Addressing gum problems early helps prevent more serious complications and supports long-term wellbeing.
How to Stop Gums from Bleeding When Brushing
Improve Your Brushing Technique
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle circular motions along the gumline. Brushing harder does not clean better, it often causes more harm.
Brush and Floss Consistently
Brush twice a day and floss once daily. Consistency is key to reducing plaque and allowing gums to heal.
Use an Antibacterial or Fluoride Toothpaste
These help reduce bacteria and strengthen enamel, supporting healthier gums.
Rinse with Salt Water or Dentist-Recommended Mouthwash
Warm saltwater rinses can help soothe inflamed gums. An antibacterial mouthwash may also be recommended by your dentist.
Quit Smoking or Vaping
Smoking reduces blood flow to the gums, masking symptoms while allowing gum disease to progress. Quitting significantly improves gum health.
When to See a Dentist About Bleeding Gums
You should book a dental appointment if:
- Your gums bleed regularly or heavily
- Bleeding lasts longer than one to two weeks
- You notice swelling, pain, or gum recession
- You have persistent bad breath or loose teeth
A professional dental clean removes plaque and tartar that can’t be eliminated at home. Your dentist or hygienist can also assess whether gum disease or another issue is present and recommend appropriate treatment.
Professional Treatments for Bleeding Gums
Depending on the cause, treatment may include:
- Professional scale and clean
- Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing)
- Periodontal maintenance
- Oral hygiene instruction tailored to your needs
Early treatment is often simple and highly effective.
Looking After Your Gum Health Long Term
Healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy smile. Maintaining good oral hygiene habits and attending regular dental check-ups can prevent bleeding gums and reduce the risk of more serious problems.
If you’ve noticed bleeding when brushing, it’s a sign your gums are asking for attention. With early care and the right guidance, most gum issues can be managed helping you keep your teeth and smile healthy for years to come.



